Connecting to aubo_control
aubo_control is the low-level robot controller running on the Embedded PC in the Control Box cabinet. When the PC boots up, the aubo control starts up as a daemon (i.e., a service) and the AuboStudio or Graphical User Interface connects as a client using a local TCP/IP connection. Programming a robot at the Script Level is done by writing a client application (running at another PC) and connecting to aubo_control using TCP/IP socket,HTTP,and WebSocket.
Supported Communication Protocols and Ports
The AUBO SCRIPT supports the following communication protocols and corresponding port numbers:
| Protocol | Port |
|---|---|
| TCP Socket | 30002 |
| HTTP | 30003 |
| WebSocket | 30003 |
Script Protocol Specification
When sending a script string to the robot controller via TCP Socket protocol, the message must end with \r\n\r\n.
Script String Example
The following example demonstrates how to send a script string via TCP Socket, HTTP, and WebSocket communication. The script is written for the AUBO i5 robotic arm.
return function(api)
local _ENV = require('aubo').sched.select_robot(1)
home = { -0.000003, -0.127267, -1.321124, 0.37694, -1.570796, -0.000008 }
move1 = { -0.400318, 0.064315, 0.547598, 3.14, 0.0, -2.63782 }
move2 = { -0.400318, 0.064315, 0.379989, 3.14, 0.0, -2.63782 }
move3 = { -0.400318, 0.064315, 0.547598, 3.14, 0.0, -2.63782 }
move4 = { -0.400319, -0.298610, 0.547598, 3.14, 0.435471, -1.57 }
move5 = { -0.400319, -0.243865, 0.429931, 3.14, 0.435471, -1.57 }
move6 = { -0.400319, -0.298610, 0.547598, 3.14, 0.435471, -1.57 }
-- Set Tool Center Point (TCP) offset relative to the flange center
setTcpOffset({0,0,0,0,0,0})
-- Set speed fraction
setSpeedFraction(0.75)
-- Joint movement
moveJoint(home, 3.14, 3.14, 0.0, 0)
-- Linear movements
moveLine(move1, 2, 1, 0.0, 0)
moveLine(move2, 2, 1, 0.0, 0)
moveLine(move3, 2, 1, 0.0, 0)
moveLine(move4, 2, 1, 0.02, 0)
moveLine(move5, 2, 1, 0.0, 0)
moveLine(move6, 2, 1, 0.02, 0)
endSending Scripts via TCP Socket
To send a script using TCP Socket, connect to the robot’s IP address on port 30002.
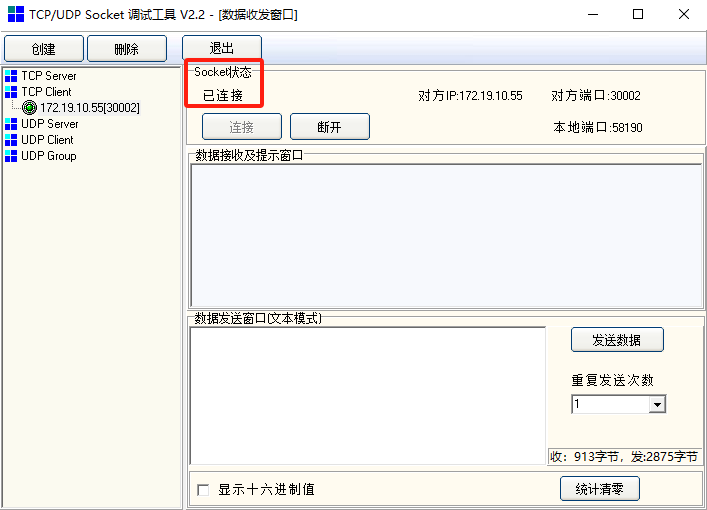
Steps using a TCP Debugging Tool:
Enter the robot’s IP address and port number, then establish a connection. Once connected, the socket status should indicate a successful connection.
Input the script string and press Enter twice at the end of the script before clicking "Send Data".
Note: The script string sent via TCP Socket must end with
\r\n\r\n. Since\r\nrepresents a newline character, pressing Enter twice ensures correct formatting.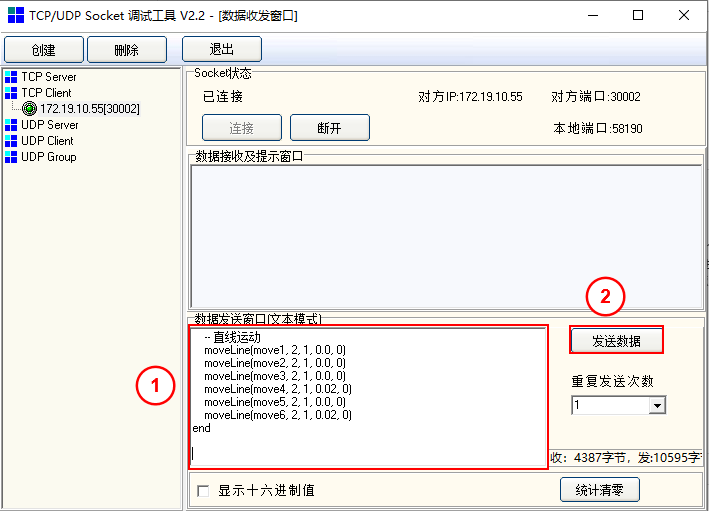
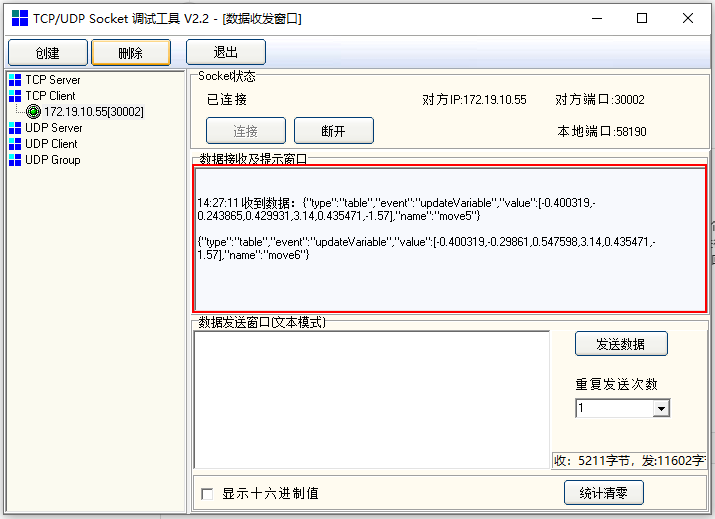
After a successful transmission, the received data will be displayed.
Sending Scripts via WebSocket
To send a script using WebSocket, connect to the URL:
ws://<robot-ip>:30003where <robot-ip> is the IP address of the robot, and 30003 is the WebSocket port number.
Steps using a WebSocket Testing Tool:
Use an online WebSocket testing tool such as EasySwoole WebSocket Test Tool.
Enter the WebSocket URL and establish a connection. Once connected, the server status should indicate a successful connection.
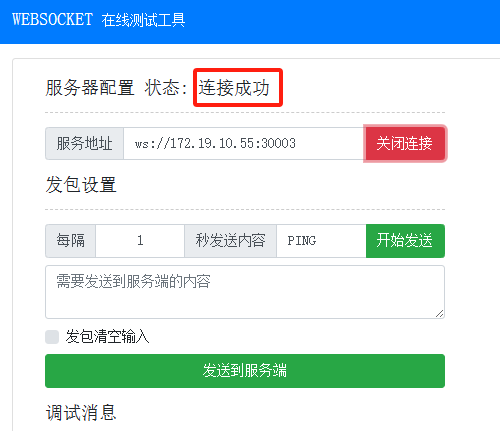
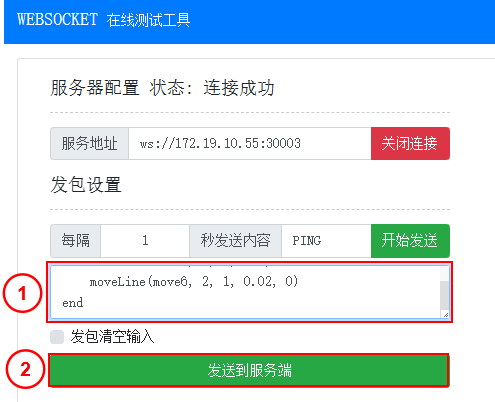
Input the script string and click Send to Server.
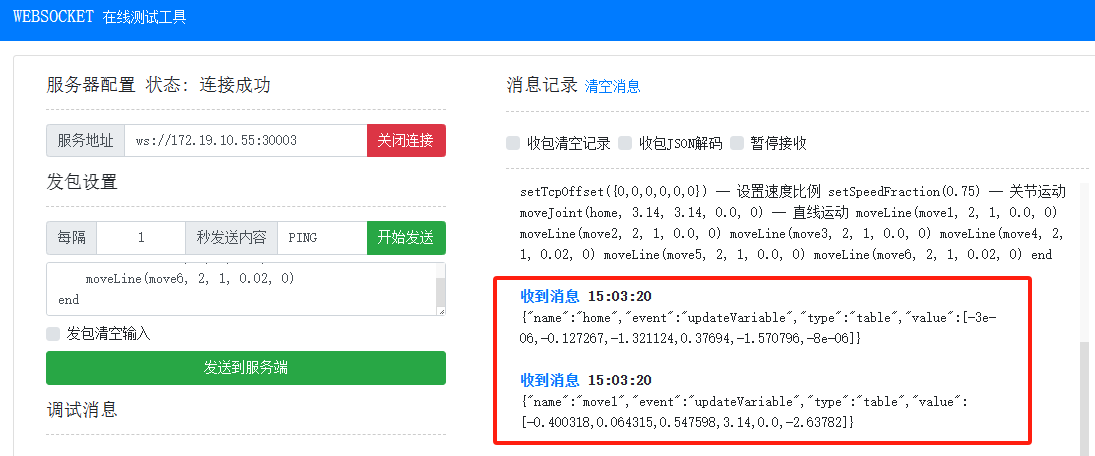
After a successful transmission, the received message will be displayed.
Sending Scripts via HTTP
To send a script using HTTP, send a POST request to:
http://<robot-ip>:30003/aubo_scriptwhere <robot-ip> is the IP address of the robot, and 30003 is the HTTP port number.
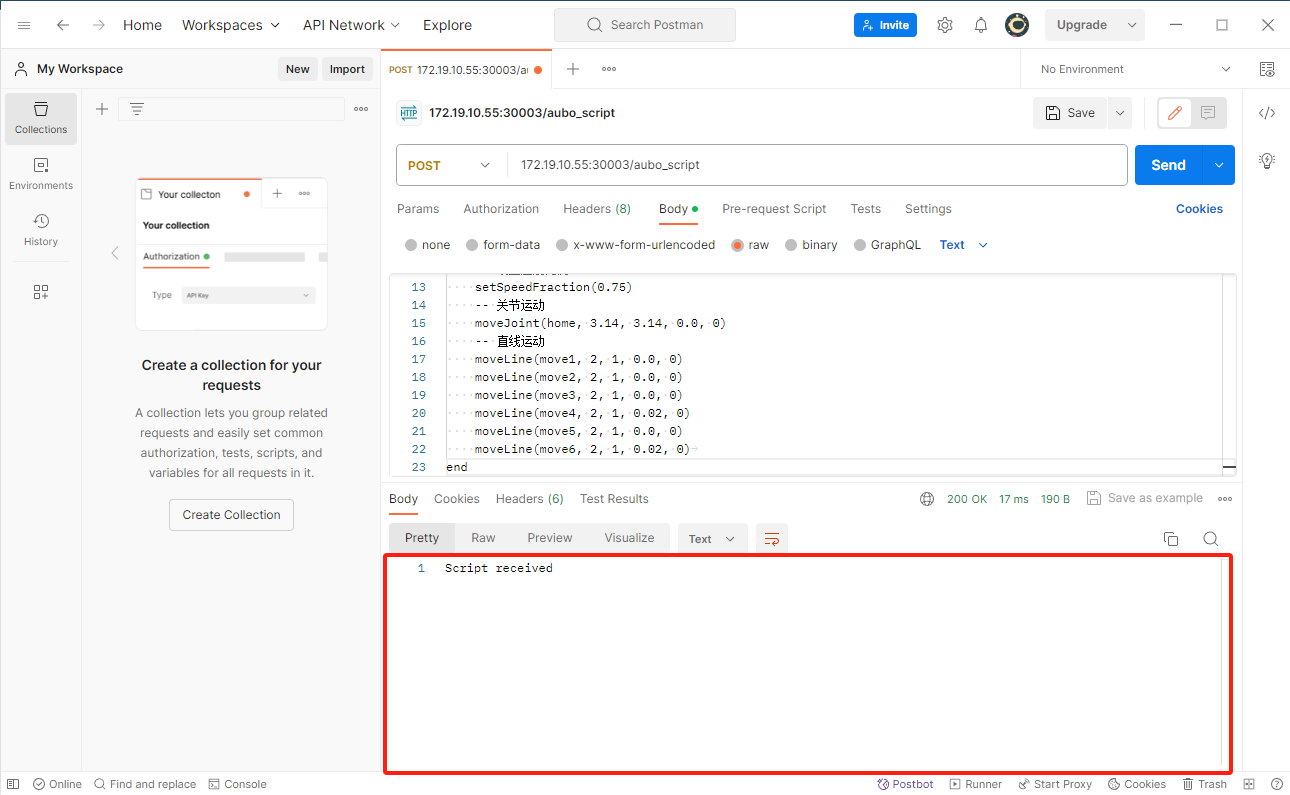
Steps using Postman:
Open Postman, select POST as the request method, and enter the URL.
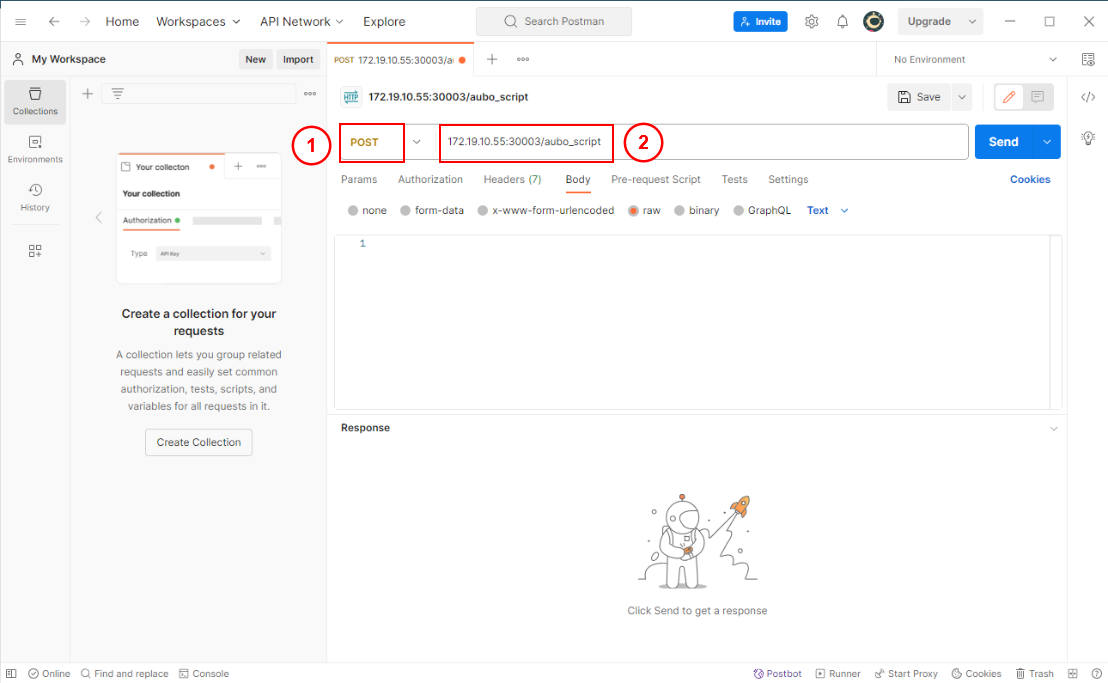
In the Body section, enter the script string and click Send.
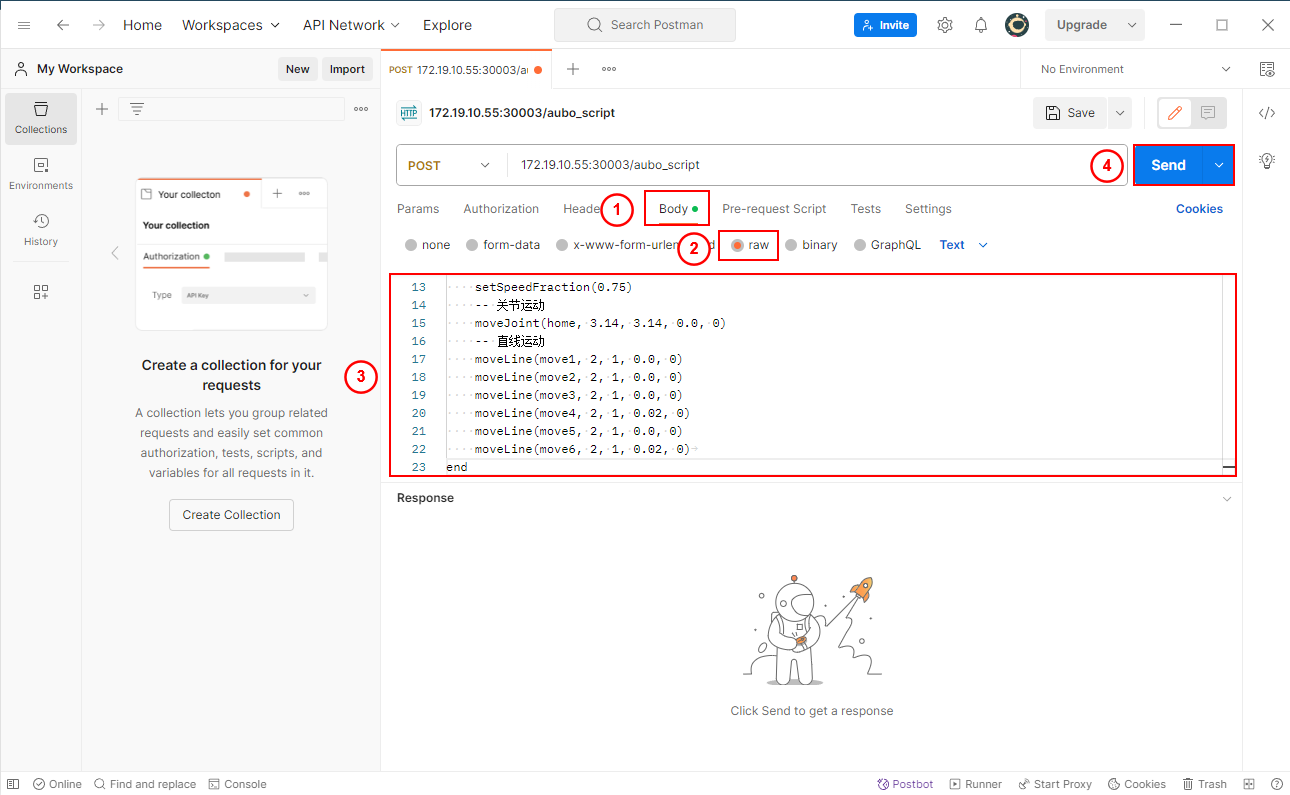
After a successful transmission, the received message will be displayed.