ARCS Network Configuration Guide
1 Three Network Configuration Methods
Configure the ARCS software network in Home > Setting > System > LAN Network Port.
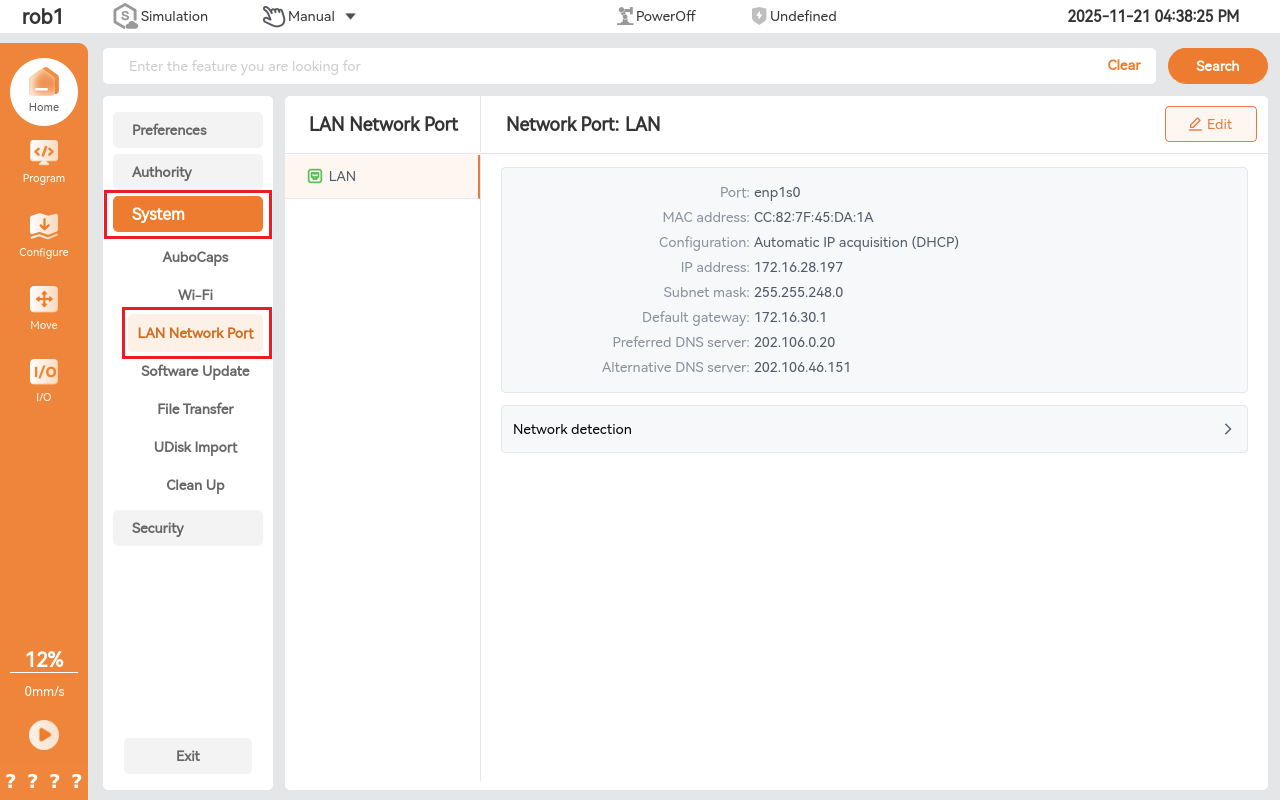
Automatic IP (DHCP)
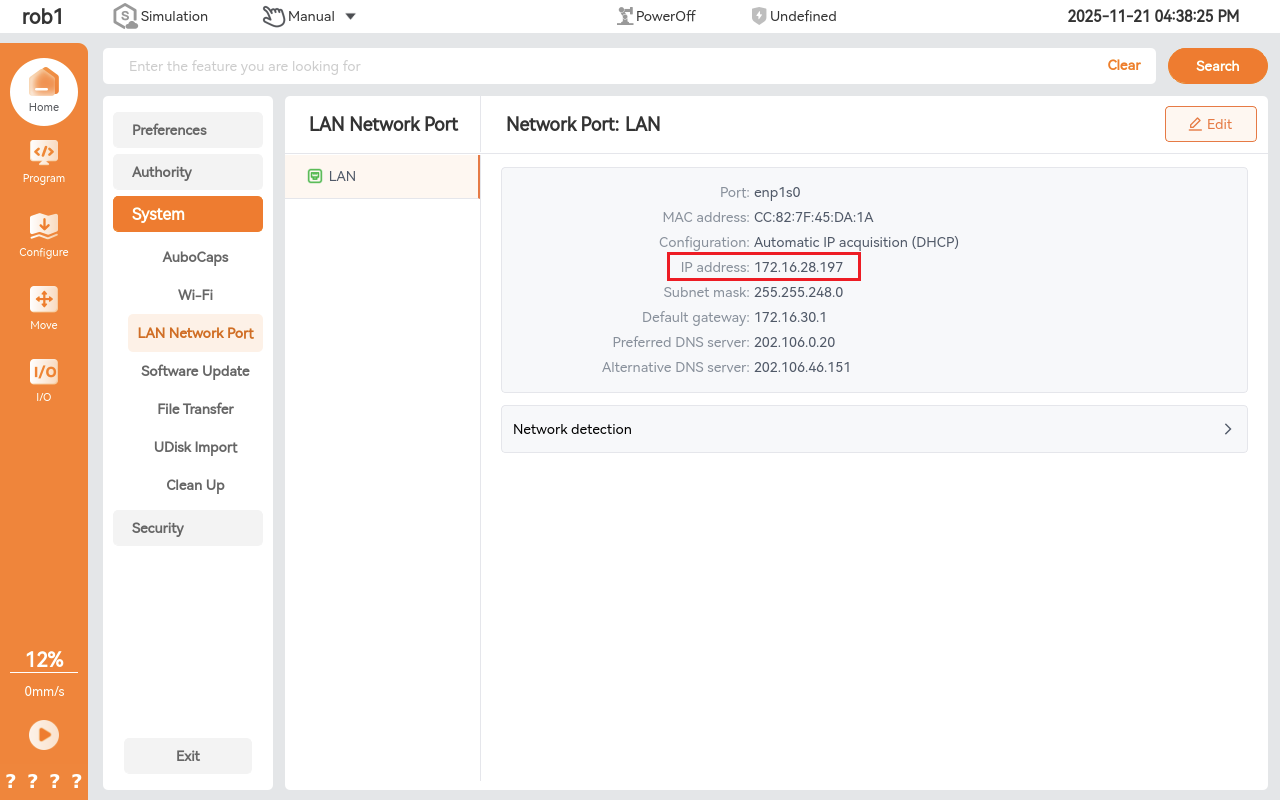
After connecting a wired network to the controller, DHCP will automatically assign an IP address. In the example below, the IP address is 172.16.24.24.
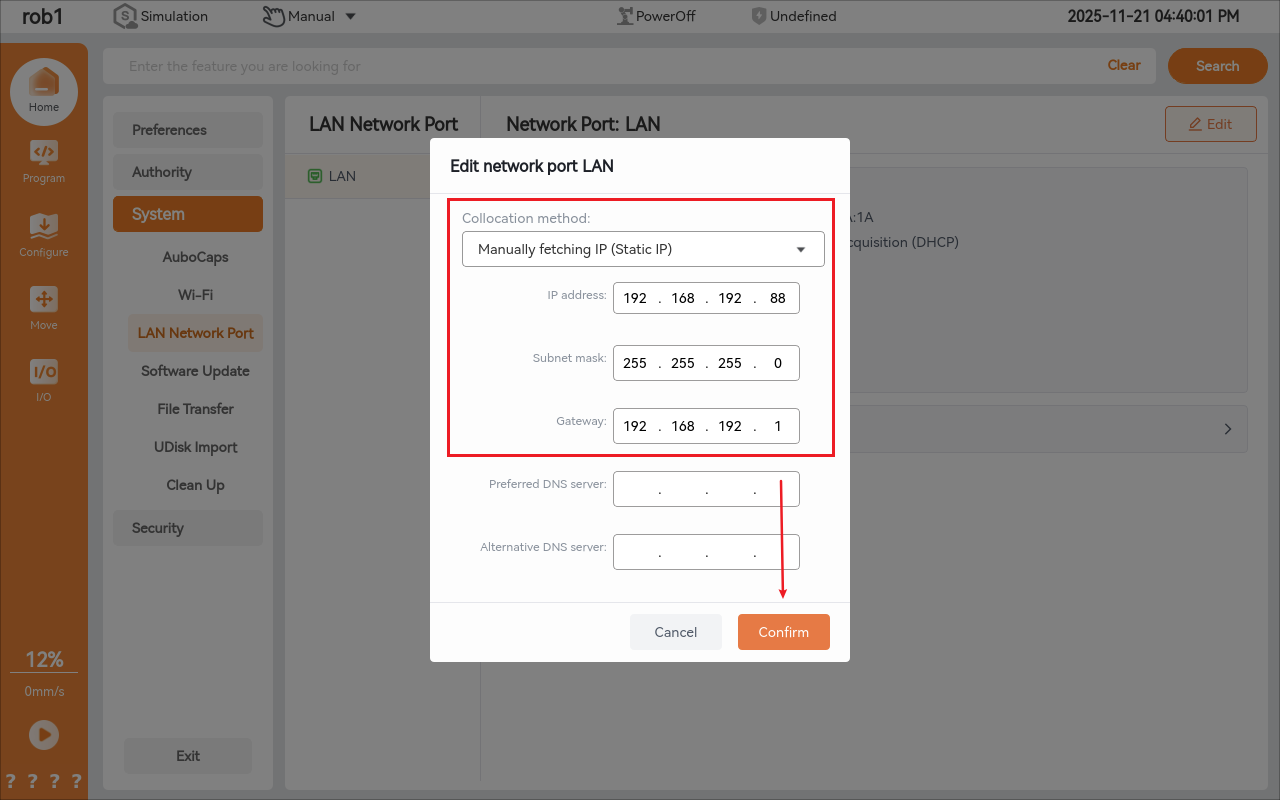
Manual IP (Static IP)
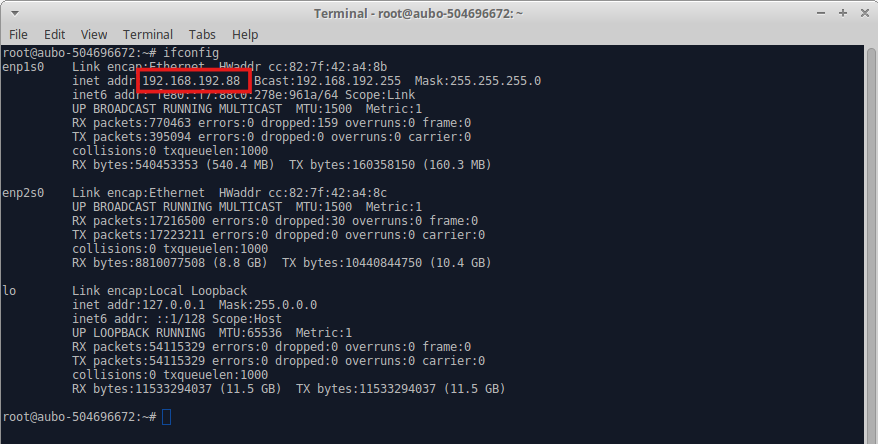
To set a fixed IP for the controller (e.g., 192.168.192.88), configure the following:
IP Address: 192.168.192.88
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway: 192.168.192.1
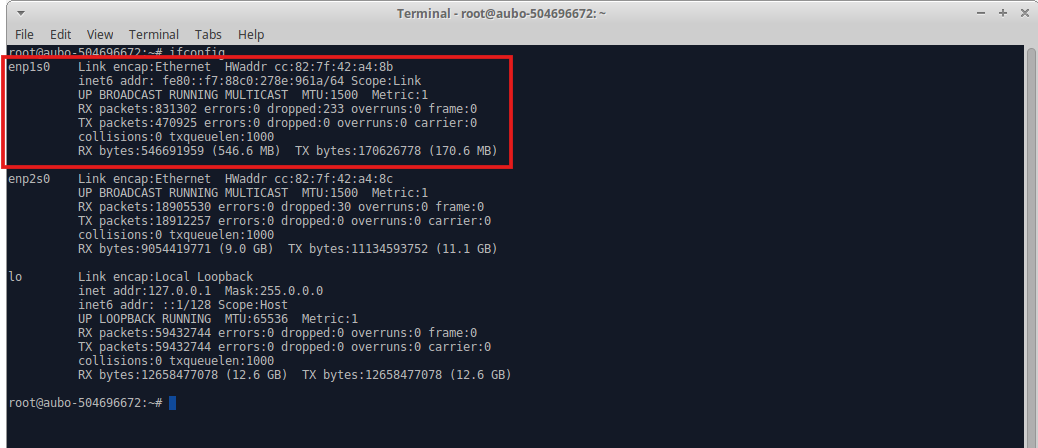
After completing the settings, click the Confirm button. As shown in the figure below, check via the terminal that the controller's IP address has been updated to 192.168.192.88.
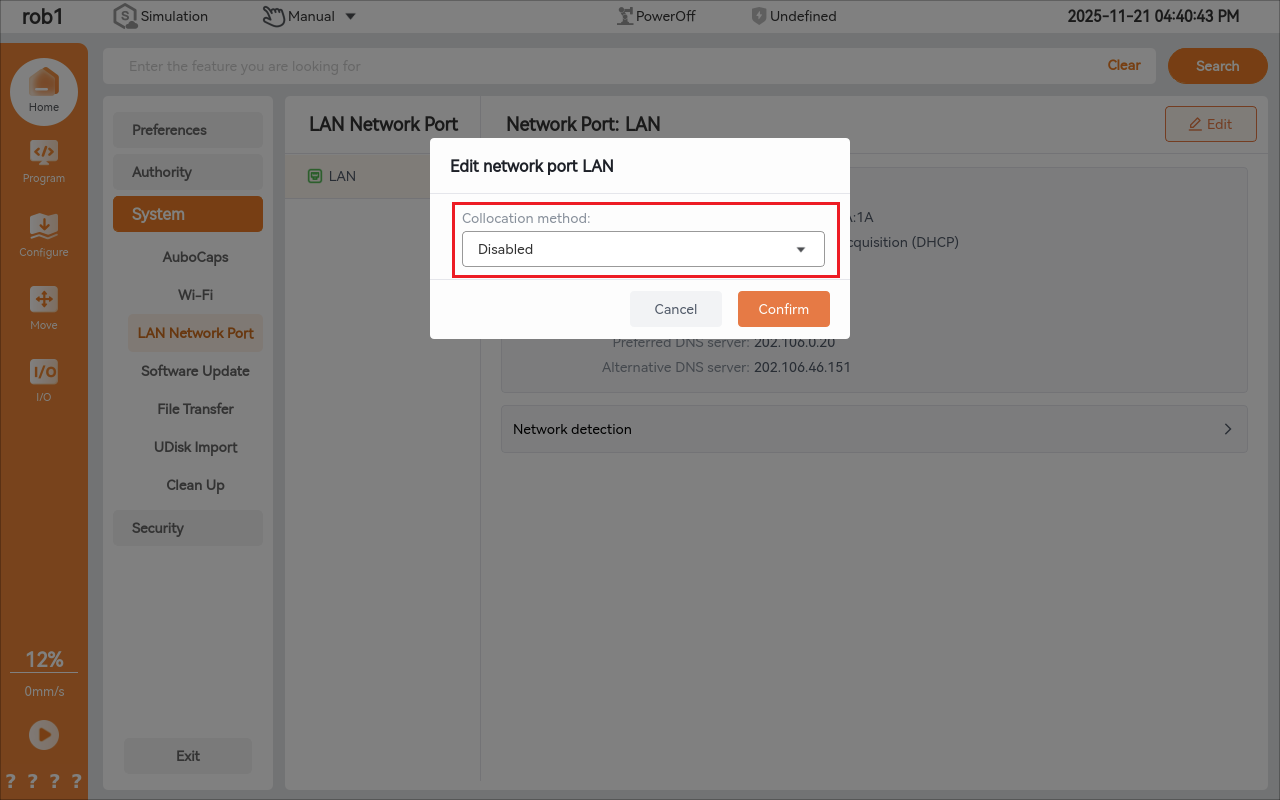
Disable
Select Disable as the configuration mode and click Confirm to disable the network.
2 IP Address Query
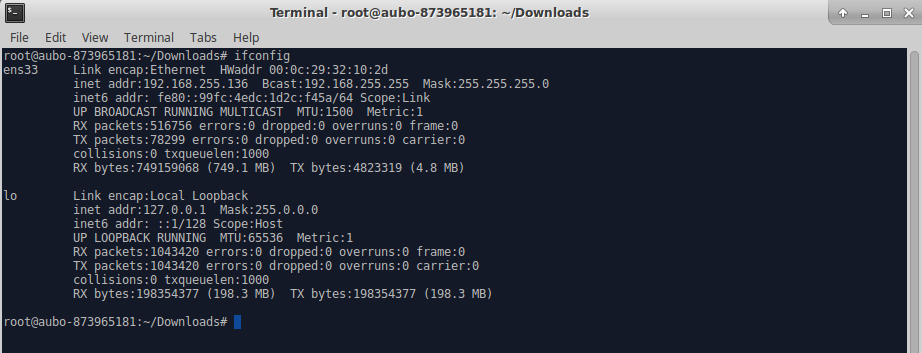
- Linux System use the
ifconfigcommand
- Windows System use the
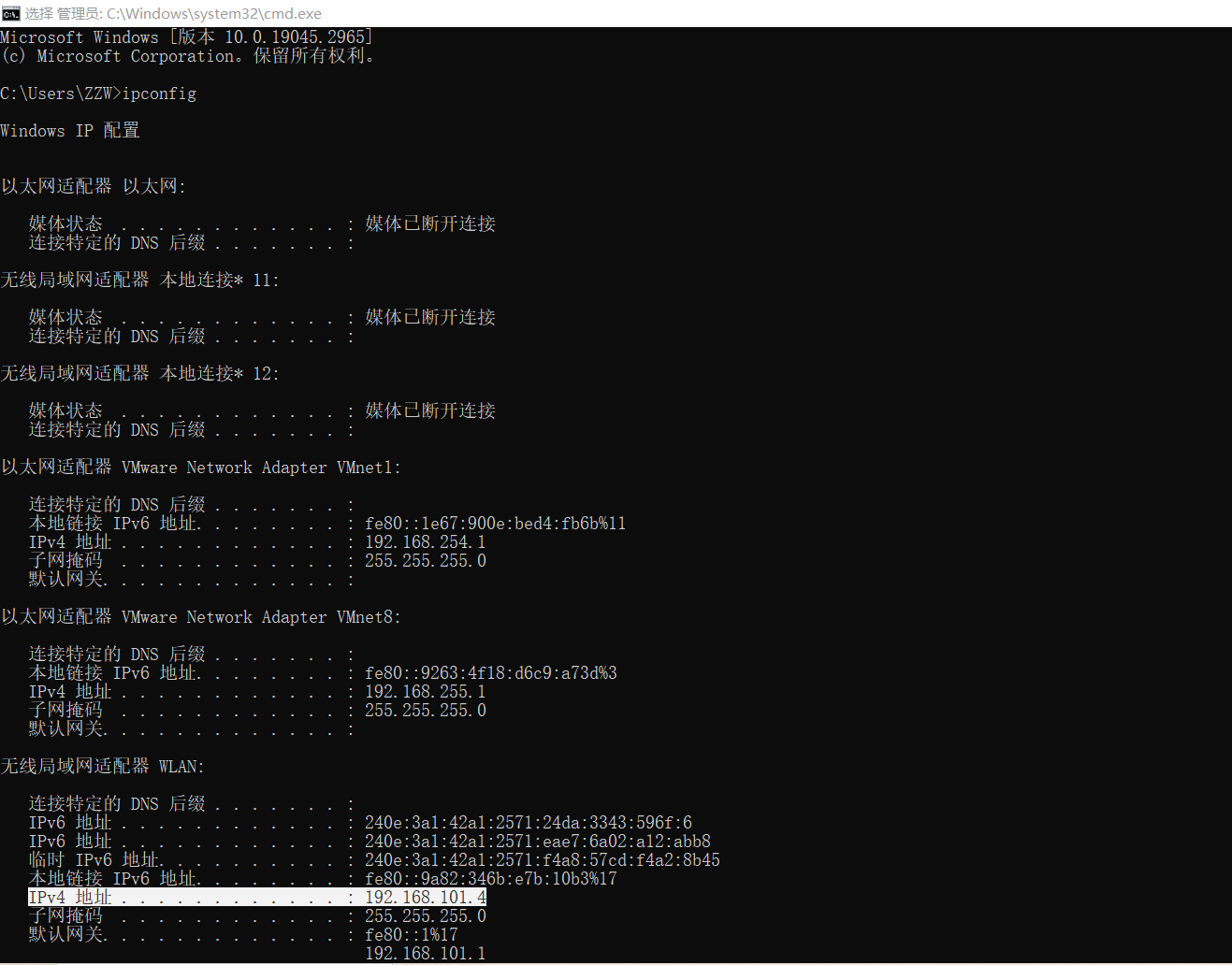
ipconfigcommand
3 Using Ping and Telnet Tools
Ping
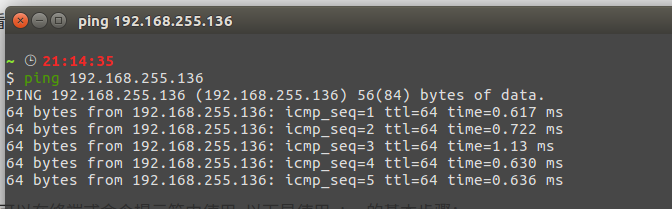
Ping is a command-line tool for testing network connectivity, usable in terminals or command prompts. Here are the basic steps:
First, open a terminal or command prompt window and enter the following command:
ping <hostname>Replace <hostname> with the hostname or IP address of the computer you wish to test. For example, to test connectivity to a computer named example.com, enter:
ping example.comA successful connection will display a series of echo messages, including the round-trip time for each packet and the packet loss rate. Pressing Ctrl+C on your keyboard will stop the ping operation.
Ping command may be blocked by firewalls or security measures. Ensure the firewall is disabled if ping fails.
Telnet
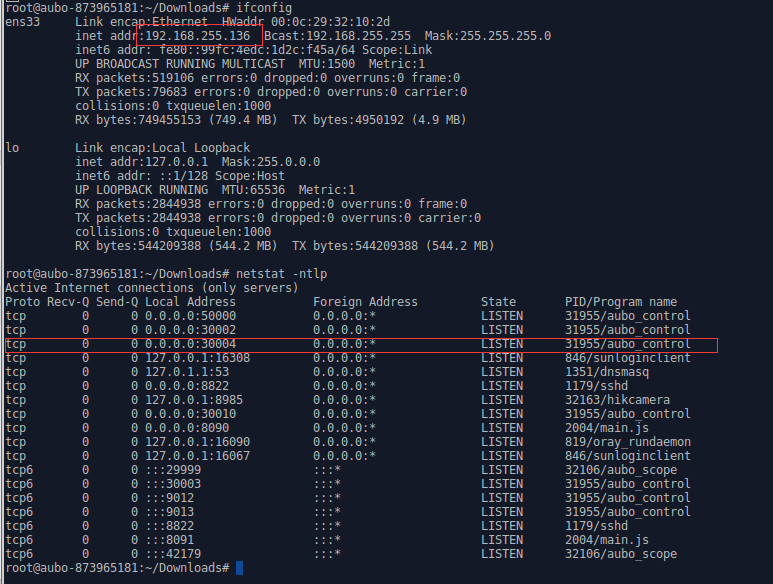
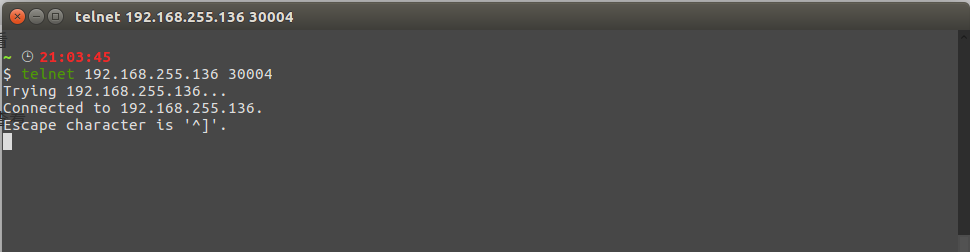
Telnet is a protocol for remote device access. Open a terminal or command prompt window and enter the following command:
telnet <hostname> <port>Where <hostname> is the hostname or IP address of the computer you wish to connect to, and <port> is the port number to connect to. For example, to connect to a web server on the computer with hostname example.com and port number 80, enter the following command:
telnet example.com 80A successful connection will display a welcome message or command prompt where you can enter commands or send data.
To close the connection, press Ctrl+] on your keyboard, then enter the quit command.
Refer to the images below for Telnet usage:
4 Disable Windows Firewall
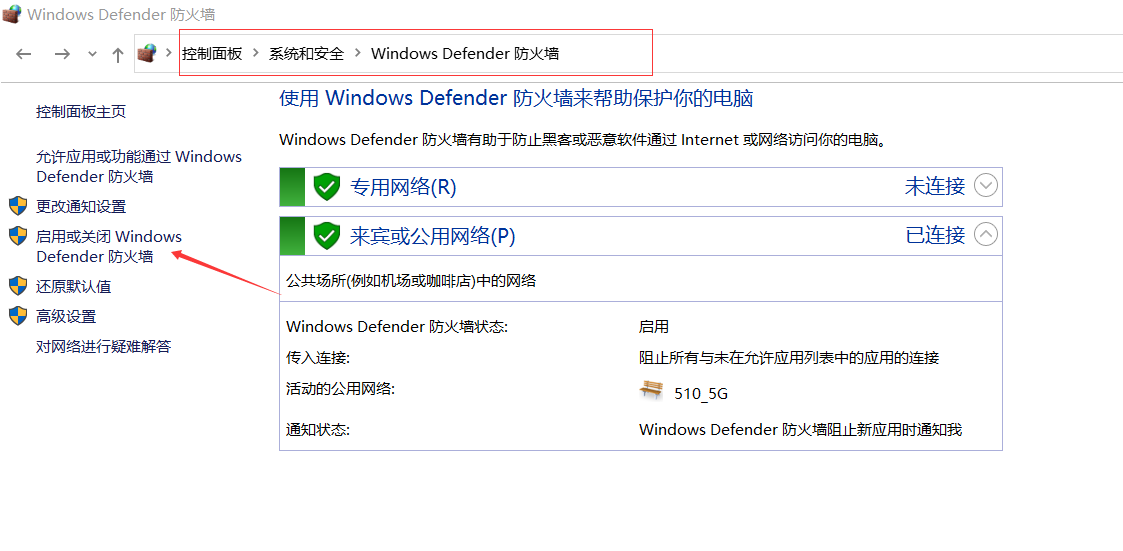
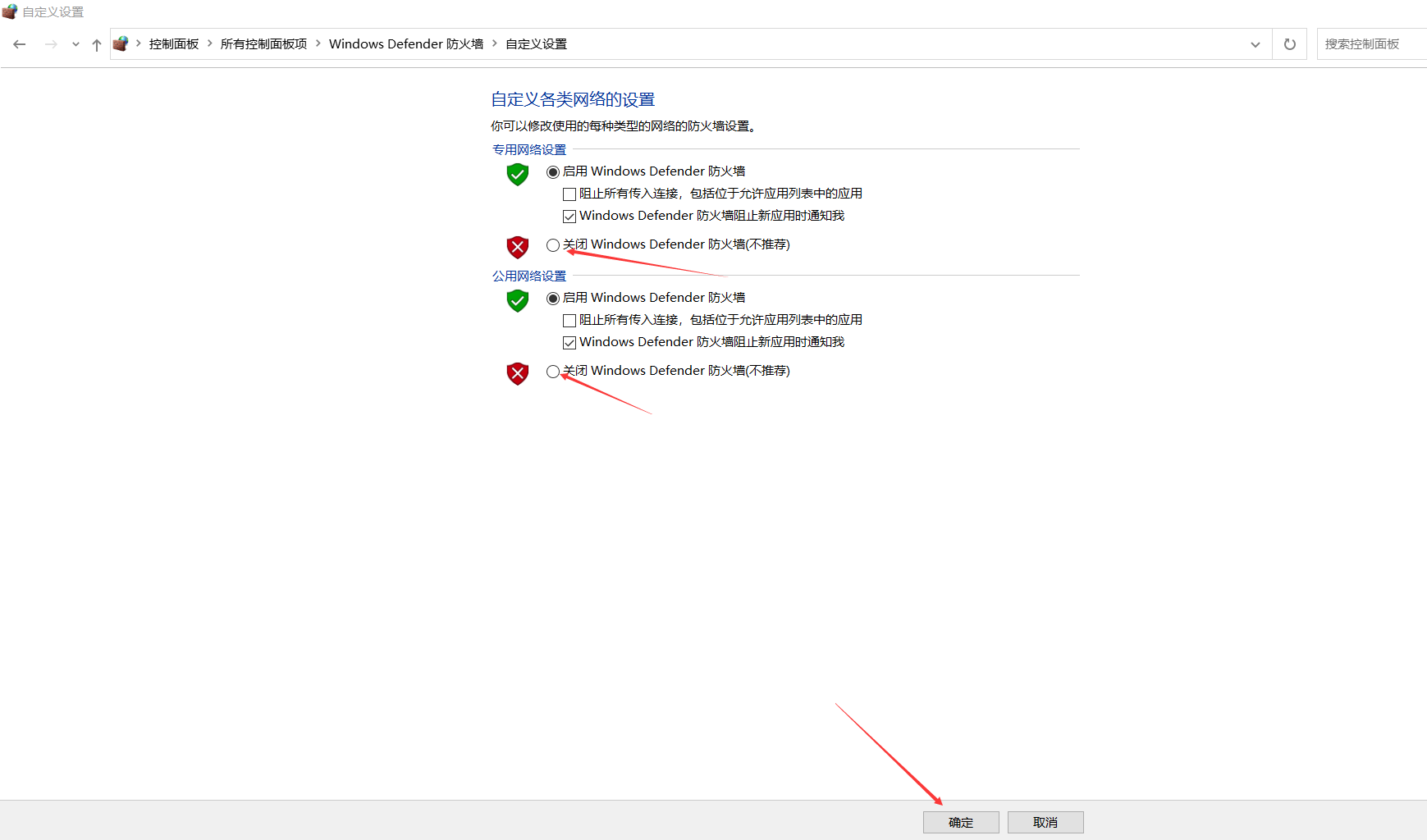
When communicating between Windows and the controller, it is recommended to disable the firewall. Refer to the images below:
5 Configure Wireless Network Adapter
Insert the wireless network adapter into the controller.
Enter
ifconfigin the terminal to verify the adapter is recognized, as shown below: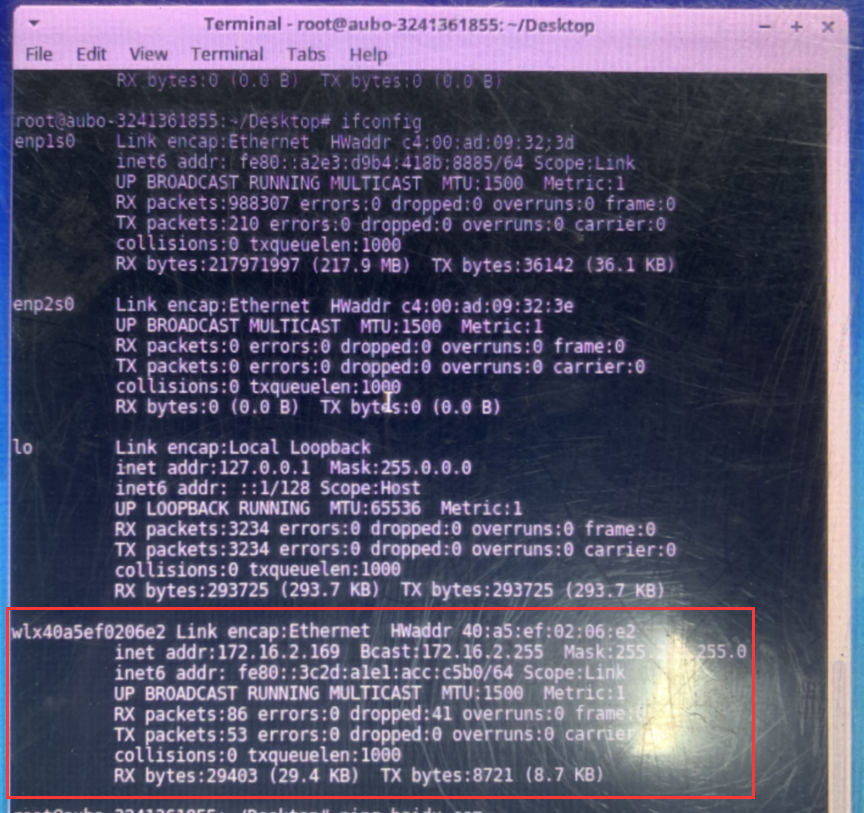
Right-click on the desktop and select Applications > Settings > Network Connections.
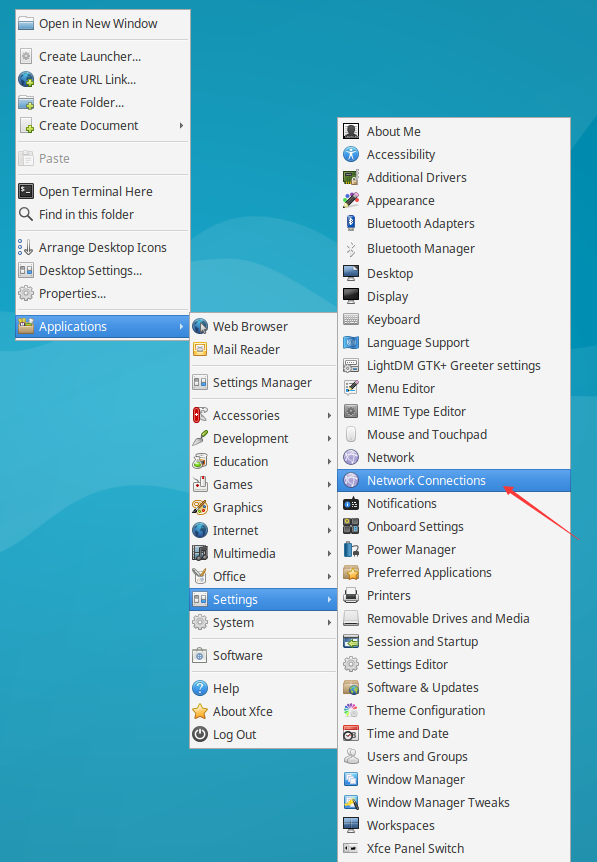
Click the Add button.
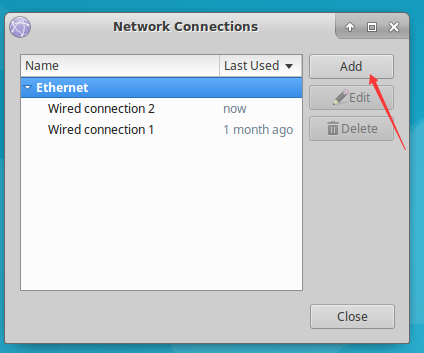
Select Wi-Fi and click Create.
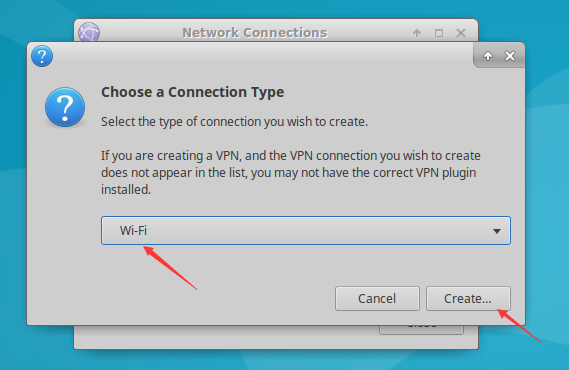
Select Wi-Fi Security, set the Security option to WPA & WPA2 Personal, and enter the Wi-Fi password in the Password field.
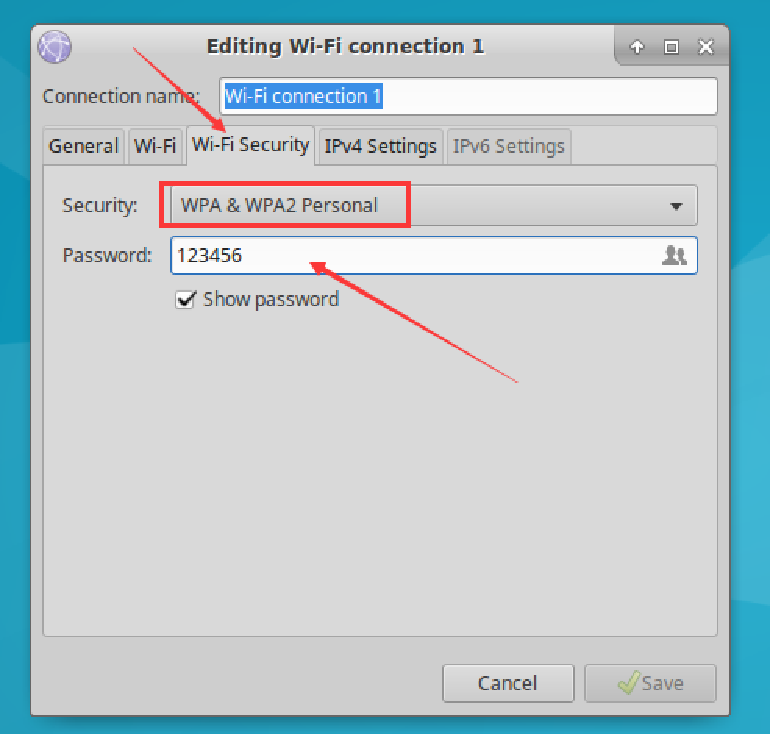
Select Wi-Fi, enter the Wi-Fi name in the SSID field (e.g.,
AUBO_Roboticsas shown in the example), and select the device address in the Device field. If no device addresses appear in the dropdown menu, it indicates the wireless network card has not successfully connected.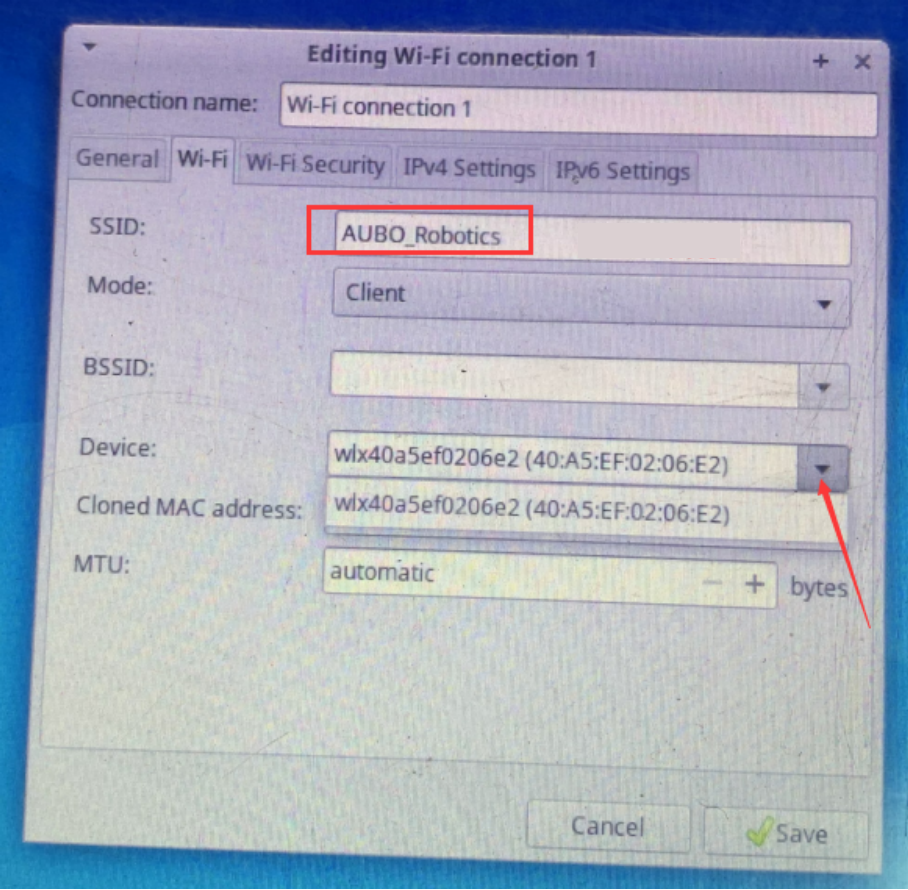
Click Save in the bottom-right corner to complete configuration.
